You can know every new products be published here, and witness our growth and innovation.
Date:09-13-2021
1). Problems with traditional zinc oxide arresters.
1. There are potential safety hidden danger at work
Currently, zinc oxide arresters are installed in conjunction with monitoring devices, and their structure is shown in the figure below.
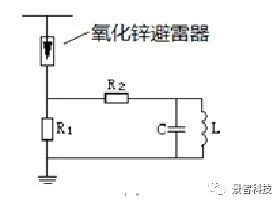
When the zinc oxide arrester operates, a certain residual pressure will be generated on R1 in the monitoring device. The residual voltage generated by different monitoring devices will be different, but according to the provisions of “AC Gapless Metal Oxide Lightning Arrester” (GB 11032), the residual voltage can reach up to 3kV. In other words, the input terminal of the monitoring device will have a residual voltage of up to 3kV when the arrester is operating. This residual voltage will be superimposed on the residual voltage after the zinc oxide arrester is activated, which increases the overall residual voltage value of the zinc oxide arrester, which has a negative effect on effectively suppressing overvoltage.For example, a lightning arrester for a substation with a rated voltage of 10kV, with a nominal discharge current of 5kA, the typical value of the residual voltage of the lightning impulse current is 27kV. If the 3kV residual voltage of the monitoring device is superimposed, the overall residual voltage of the arrester will reach 30kV, and the residual voltage will increase by 11.1%, which will seriously change the operating characteristics of the arrester and weaken the arrester’s effect of suppressing overvoltage.
In order to facilitate the operation personnel to check and record the data, the zinc oxide arrester monitoring device is generally installed at a position about 1.8m from the ground. If there is a maximum voltage of 3kV at the input of the monitoring device, there will be a major safety hazard to the personal safety of the work.
2. There are hidden dangers in operational reliability
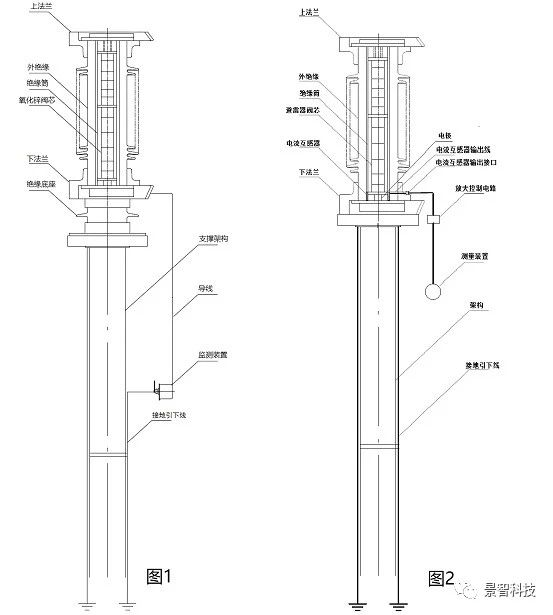
The wiring of the traditional zinc oxide arrester and detection device is shown in Figure 1 below. Among them, the insulating base, the wire, and the monitoring device are all additional equipment for realizing the measurement of the leakage current of the zinc oxide arrester under the operating voltage. These devices are not necessary for the normal operation of the zinc oxide arrester itself. The addition of these additional equipment increases the probability of equipment defects. Regardless of which equipment has a defect, it may cause the arrester to stop operating and affect the stability of the equipment operation. For example, in the actual work, the insulating base often has problems of dampness, abnormal insulation or damage, which will affect the operation and monitoring of the arrester.
According to online statistics, among the serious and critical defects of zinc oxide arresters in a certain year, there were 21 abnormalities in the body, 110 abnormal leakage currents, 13 abnormal external insulation, 1 abnormal base (flange), 8 abnormal conductors, and 10 drainage line problems. The monitoring device was abnormal 183 times. It can be seen that the additional equipment will have a significant impact on the stable operation of the arrester. Another statistical data shows that a total of 2,509 defects occurred in lightning arresters of 110 (66) kV and above in a certain year, of which the defects of the arresters due to abnormal leakage current measurement accounted for 31.79% of the total number of defects, and the defects of monitoring devices accounted for 52.89%.